10+ diagram of replication fork
What is the purpose of a replication fork. The proliferation of all organisms depends on the coordination of enzymatic events within large multiprotein replisomes that duplicate chromosomes.

Model Of A Replication Fork Showing Leading And Lagging Strand Download Scientific Diagram
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES ResearchGate the.
. DNA replicates in a semi-conservative manner in which each individual strand is copied to form a new molecule of DNA. The two strands can be labelled with isotopes using substrates that. Replication begins at an origin of replication where two strands are separated opening a replication bubble.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda MD 20894 USA. The replication fork is a structure that is opened by DNA helicase within the long helical DNA during DNA replication.
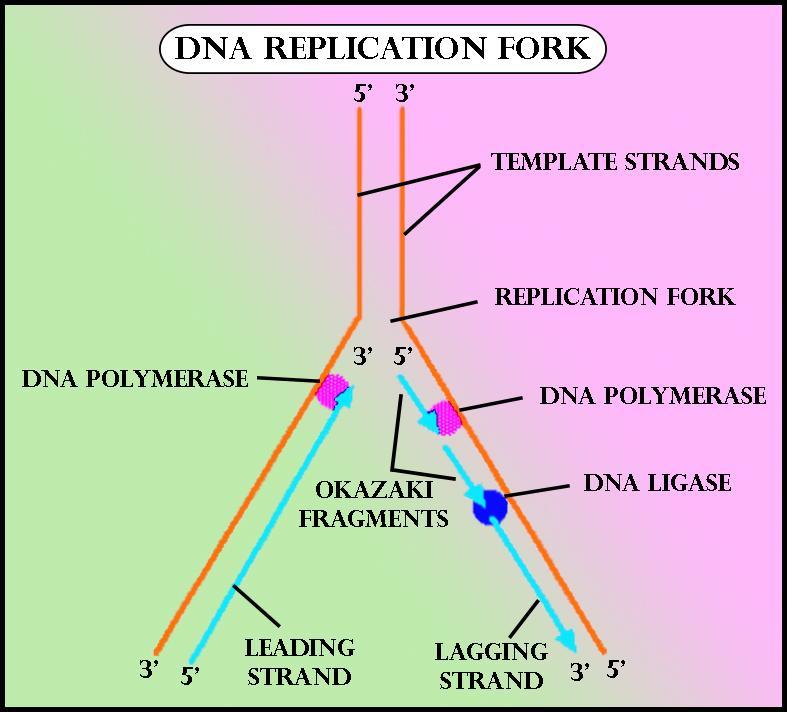
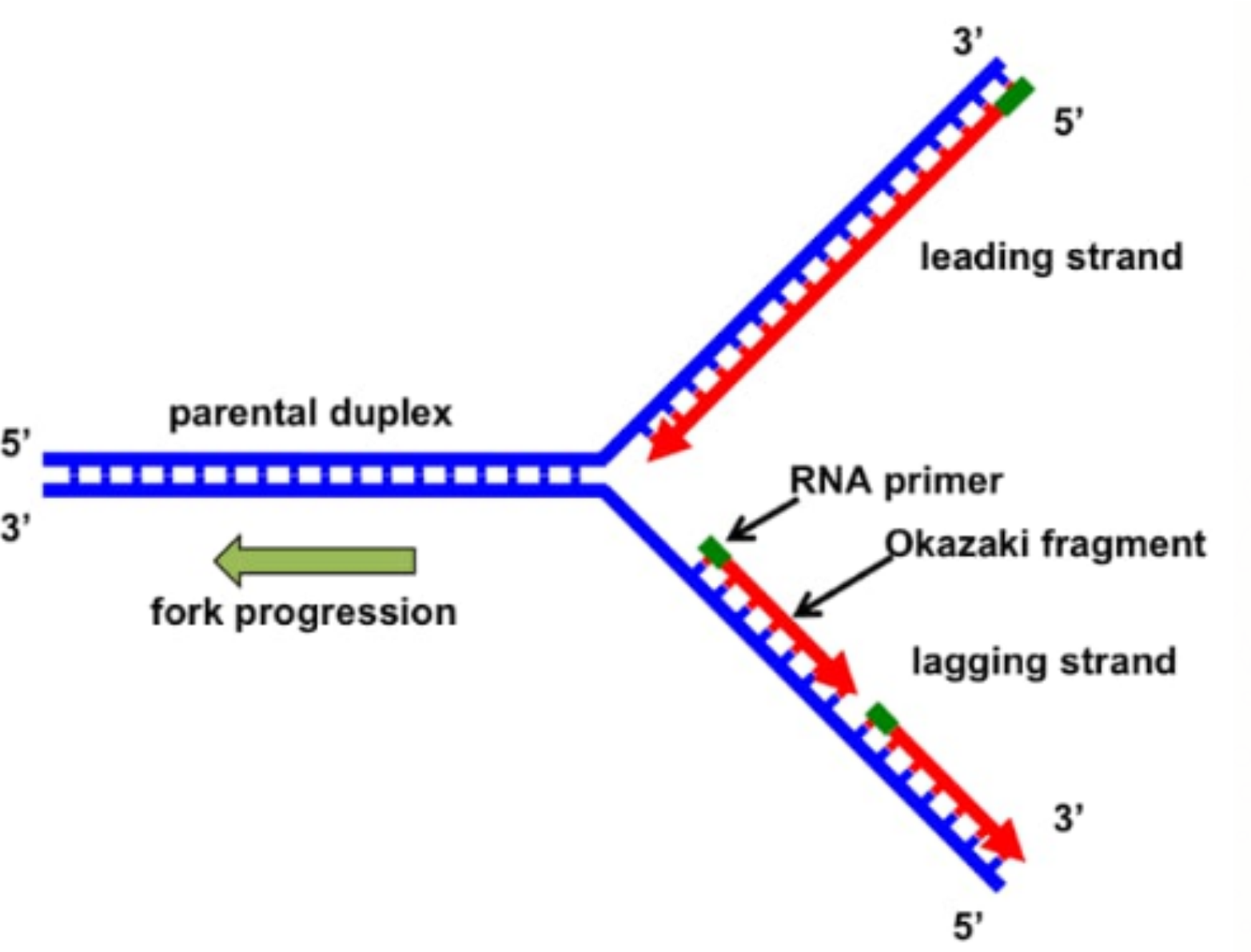
The replication fork is a region where a cells DNA double helix has been unwound and separated to create an area where DNA polymerases and the other enzymes involved can use each strand. DNA Replication Steps. The replication fork is two-way.
Replicating fork is the structure of the DNA double helix after the unzipping by ligase enzyme. This leads to two strands called leading and lagging strands. A eukaryotic chromosome may have hundreds or thousands of origins of.
Origin of replication and movement of replication fork from publication. Download scientific diagram 10. Diagram out the replication fork.
National Library of Medicine. It has two branching prongs each of which is made up of. DNA replicates in a semi-conservative manner in which each individual strand is copied to form a new molecule of DNA.
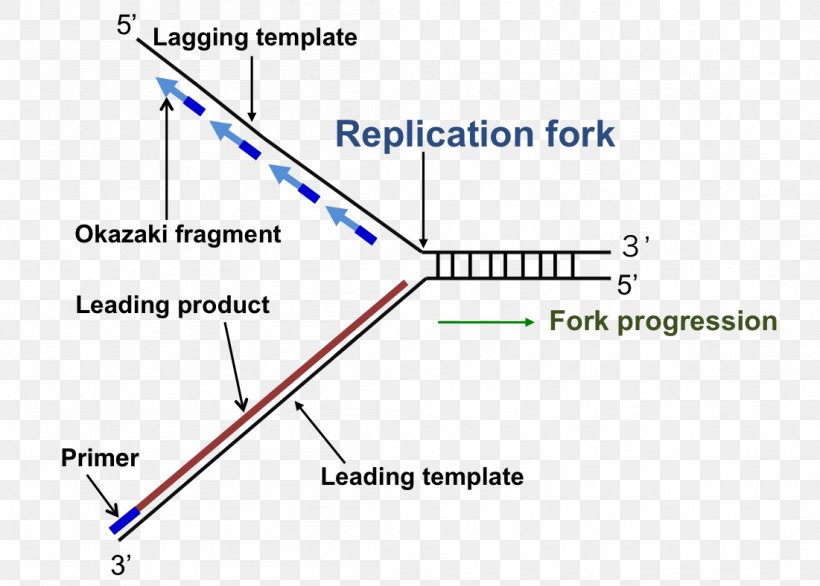
It forms at the repication bubble with the help of the enzyme DNA helicase. The replication fork is a Y-shaped structure. Synthesis of leading and lagging strands.
1 mark Direction of fork movement 5 b. The leading strand is directed from 3 to 5 The lagging strand is orientated from 5 to 3 The two sides are reproduced using two distinct. Explain why DNA replication is discontinuous on one strand.
National Institutes of Health. Why is eukaryotic DNA replication more complex than prokaryotic DNA replication 12. In the following diagram of a replication fork which DNA strand a or b is a.
The two strands can be labelled with isotopes using substrates that. Start studying Replication Fork Diagram. The template for the synthesis of the lagging strand.
Dna Replication Replication Fork Enzyme Triangle Png 1101x788px Dna Replication Diagram Dna Enzyme Parallel Download Free
Draw A Labeled Diagram Of A Replicating Fork Class 12 Biology Cbse

Mink1 Regulates B Catenin Independent Wnt Signaling Via Prickle Phosphorylation Molecular And Cellular Biology

Sampath Amitash Gadi Amitashsampath Twitter

Draw A Labelled Diagram Of Replicating Fork

Senescence In Yeast Is Associated With Chromosome Xii Cleavage Rather Than Ribosomal Dna Circle Accumulation Biorxiv
Draw A Labelled Schematic Sketch Of Replication Fork Class 11 Biology Cbse

Dna Replication Fork Biology Lessons Teaching Biology Dna Activities

K Nex Education Dna Replication And Transcription Set 525 Pieces Ages 10 Science Educational Toy History Lesson Plans Dna Lesson Plans Dna Lesson
Replication Fork Y Fork Intermediate Molecular Biology

Tolerance Of Deregulated G1 S Transcription Depends On Critical G1 S Regulon Genes To Prevent Catastrophic Genome Instability Sciencedirect

T Cell Cross Reactivity And The Herd Immunity Threshold Climate Etc
What Is A Primer In Dna Replication Quora

Maintaining Genome Stability At The Replication Fork Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology

Replication Fork How To Draw Replication Fork In Exam Replication Fork Diagram For Class 12 Youtube
Frontiers Genetic Regulation Of Vertebrate Forebrain Development By Homeobox Genes

Eukaryotic Dna Replication Wikiwand